Organizations looking to break beyond the limitations imposed by traditional cloud-based networks can find significant advantages in edge computing.
While cloud computing remains crucial in modern network architecture, the exciting possibilities offered by Internet of Things (IoT) devices, which process data closer to the source, are forcing companies to rethink their IT infrastructure strategies.
What is Edge Computing?
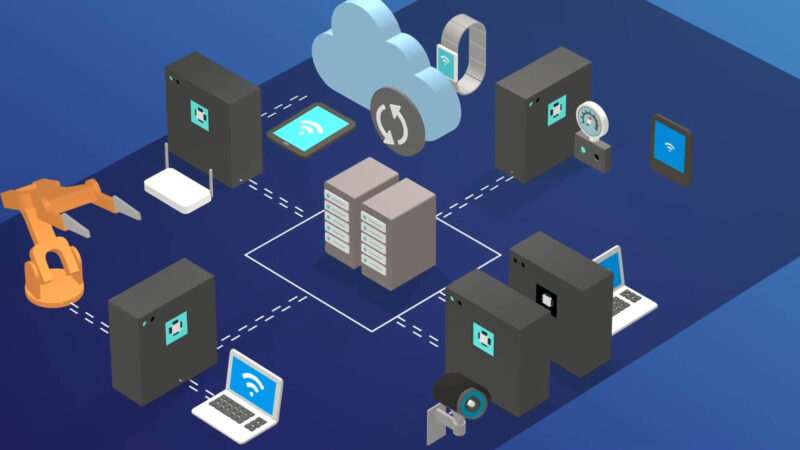
Traditional cloud networks are highly centralized. Data is gathered at the edges and transmitted back to main servers for processing. This setup originated because early edge devices lacked the computational power and storage capacity to process the data they collected. Even as connectivity improved through cellular and WiFi, the devices’ capabilities remained limited by their hardware.
With advancements in processing and storage technology, the network architecture landscape has transformed. Today’s IoT devices can gather, store, and process more data than ever before. This shift allows companies to optimize their networks, relocating processing functions closer to where data is gathered. By analyzing and applying data in real-time at the network edge, latency is reduced, and performance is enhanced.
It reduce the distance data must travel to be processed, resulting in lower latency and improved performance. This flexibility creates new possibilities for organizations aiming to optimize their IT infrastructure and deliver superior services.
The Five Key Benefits of Edge Computing
1. Speed

Speed is crucial for any business’s core operations. In the financial sector, milliseconds can make a difference in high-frequency trading algorithms. In healthcare, delays can be life-threatening. For data-driven services, lagging speeds frustrate customers and damage brands. Speed is now a best practice rather than just a competitive advantage.
It significantly increases network performance by reducing latency. IoT edge devices process data locally or in nearby edge data centers, eliminating the need to transmit data over long distances. This results in higher speeds for end-users, with latency measured in microseconds rather than milliseconds. Considering the substantial costs associated with latency or downtime, the speed advantages of edge computing are paramount.
2. Security
While IoT edge devices increase the network’s overall attack surface, they also provide important security benefits. Traditional cloud architecture is centralized, making it vulnerable to distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks and power outages. Edge computing distributes processing, storage, and applications across multiple devices and data centers, enhancing security by making it difficult for any single disruption to compromise the entire network.
Edge computing reduces the amount of data at risk by processing more information on local devices. Even if a device is compromised, it contains only the locally collected data, not the vast amounts stored in a central server. Edge data centers offer additional security measures to protect against cyber threats, ensuring robust network security.
3. Scalability
As companies grow, their IT infrastructure needs evolve. Building a dedicated data center is expensive and challenging to plan for future growth. Traditional private facilities constrain growth, potentially hindering business opportunities. Cloud-based technology and edge computing offer scalable solutions, allowing businesses to expand their computing capacity through IoT devices and edge data centers.
Edge computing facilitates cost-effective scalability by combining colocation services with regional edge data centers. Companies can expand their edge network reach quickly and efficiently, adapting to evolving markets and scaling their data and computing needs.
4. Versatility
The scalability enhances its versatility. Partnering with local edge data centers allows companies to target desirable markets without investing in expensive infrastructure. This is valuable for content providers delivering uninterrupted streaming services and enables companies to shift markets as needed.
This advanced technology empowers IoT devices to gather vast amounts of actionable data. This data can be processed locally or delivered back to the core network for advanced analysis. Armed with insights from edge networks, companies can make informed decisions and meet market demands more efficiently. Purpose-designed devices offer innovative possibilities for expanding network reach, particularly in regions with limited connectivity.
5. Reliability

Edge computing enhances network reliability. With IoT edge devices and edge data centers closer to end-users, network issues in distant locations are less likely to affect local customers. It reduce the data flowing to and from the primary network, lowering latency and speeding up overall performance.
Distributing processing functions among multiple edge data centers ensures a faster, seamless experience for users. If one path fails, data can be rerouted, maintaining service continuity. This comprehensive edge architecture provides unparalleled reliability.
Making the Edge Computing Business Case
Edge computing offers substantial benefits for businesses seeking to optimize their IT infrastructure. The key advantages include increased speed, enhanced security, improved scalability, greater versatility, and better reliability. By processing data closer to the source, edge computing reduces latency, enhances performance, and provides robust security measures.
Organizations can scale their operations more efficiently, targeting new markets and adapting to changing conditions without the heavy footprint of traditional infrastructure. The ability to gather and analyze data at the edge enables companies to make informed decisions and deliver superior services.
The Future of Edge Computing
Edge computing is set to play a critical role in the future of network architecture. As the number of IoT devices grows, the demand for faster, more efficient services will push organizations to improve their edge networks. Companies that invest in edge computing today will be well-positioned to leverage its benefits and stay ahead of competitors.
By shifting data processing to the edge, companies can optimize their networks, provide flexible and reliable service, and enhance customer experiences. Edge computing offers several advantages over traditional network architecture and will continue to be essential for businesses moving forward.
Conclusion
Edge computing provides significant advantages for businesses looking to optimize their IT infrastructure. By processing data closer to the source, companies can reduce latency, enhance performance, and improve security. The scalability and versatility allow organizations to target new markets and adapt to changing conditions efficiently.
Investing ensures that companies can leverage its benefits and stay ahead in a competitive landscape. With the growing number of IoT devices, the future holds exciting possibilities for innovation and growth.
This technology represents a transformative approach to network architecture, offering substantial benefits that will continue to drive its adoption and evolution in the coming years.
Related Posts:
- Unlocking Potential: 5 Benefits Of Python Coding For…
- Edge Computing vs. Cloud Computing: What You Need to Know
- The Future of Quantum Computing and Cryptocurrency:…
- How to Reduce Latency With Edge Computing and…
- Bridging Construction and IT: Building Smart…
- How Does Edge Computing Reduce Latency For End…








