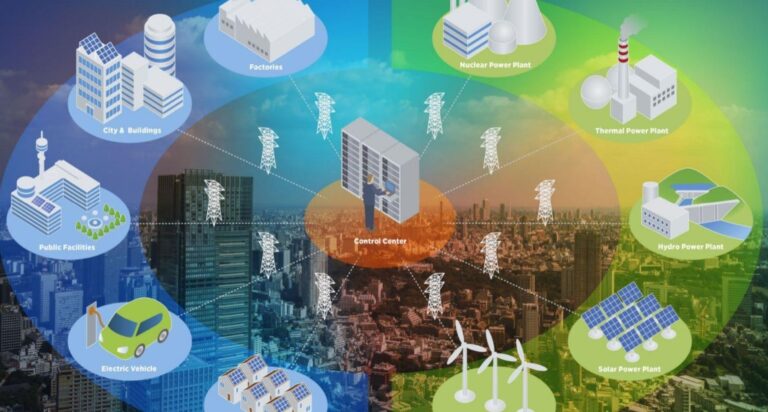
In today’s business climate, growth and scalability is essential, as well as the ability to meet industry security compliance benchmarks. As a result, utilizing a data center has become a necessity for many organizations. However, businesses want to be careful. You’re entrusting critical data and performance reliability to a partner who holds, in many cases, your reputation in their hands.
For that reason, when an organization performs a data center assessment, they should do so with full knowledge of the technology trends that have impacted the way modern data centers are designed and managed. Data center tech is an important differentiator for colocation facilities, which offer their customers data center technology that is far beyond the reach of many small or even medium-sized companies. Understanding how data center technology trends can benefit their customers is vital to choosing the best colocation partner.
Quick Links
- What is a Data Center?
- Data Center Setup
- Data Center Trends: Where the Data Center Industry is Now and Where it’s Heading
- 8 Important Developments in Data Center Technology
- Experience the Latest in Data Center Trends with vXchnge
What is a Data Center?

In simple terms, and perhaps the broadest sense, a data center is typically a centralized location, which can be off or on-premise, that houses the hardware and networking components required to maintain and support an organization’s applications and software. As noted, these centers may be on-premise, which means an organization houses and handles their own data center or they can be off-premise which typically means a colocation service.
However, because of the logical and physical security requirements, not to mention maintenance, staff, and power required, many businesses choose an off-premise data center handled by a colocation service provider who then tends to all of those issues. The advantage here is that not only does a business get all of those services included, but they can also leverage a colocation data center’s scalability and the expertise of the IT professionals who work there to assist with infrastructure needs and concerns.
Data Center Setup
Of course, a data center is more than just a space, more than just a physical location that has room to house all of the stacks, servers, and hardware required to manage a network, store data, and support the applications of the businesses it serves.
Ideally, this facility has room for growth and must have the capacity to handle that growth as well as the ability to account for the physical security of the equipment. In other words, the facility should be prepared to regulate environmental conditions and withstand any potential external environmental factors such as storms, flooding, etc. through backup power supplies, and actual building infrastructure.
In addition to the physical space and facility needs, the data center stores all of the IT hardware, software, and other equipment needed to maintain services. This is, of course, accompanied by support infrastructure that manages issues related to environmental controls and redundancies.
The final component is the staff who manage the facility and oversee management, maintenance, and client needs ensuring that the uptime guaranteed on Service Level Agreements (SLA) is met.
Data Center Trends: Where the Data Center Industry is Now and Where it’s Heading

Let there be no doubt that the future is driven by data. Nearly every industry, across every vertical is managing, handling, sending and receiving data, and then using that data to drive their business strategies.
So while some data center technologies, infrastructures, and services, like the ones discussed below, are just starting to gain a foothold in the industry, the needs of modern businesses will likely drive those to the forefront.
Colocation used to be optional, but with the movement of whole sectors to remote work and consumer reliance on online transactions and connections, the demand for network reliability and scalability will only continue to grow, meaning colocation is the future. Further, with more businesses realizing how data can and will shape their industries, expect reliance on data centers to grow.
8 Important Developments in Data Center Technology

1. Data Center Storage Solutions
Data center storage is one of the most pressing concerns facing today’s companies. The US alone generates over three million gigabytes of data every minute, and the increasing reliance on big data analysis makes data storage more important than ever. This pressure has led many companies to invest in hard drive technology, increasing the performance of existing storage formats while working to develop new formats.
For many years, hard disk drives (HDDs) were the go-to solution for data storage thanks to their reliability and low cost. Unfortunately, this technology has largely reached its performance limits. Solid state drives (SSDs) have yet to reach price parity HDDs, but flash memory has made significant strides in both capacity and access speed.
As more organizations turn to SSDs for improved performance, data centers will also be able to use the technology to help colocation customers store and access data more effectively.
2. Server Virtualization

In an effort to reduce infrastructure burdens, many data centers and managed service providers (MSPs) have shifted to a software defined data center (SDDC) service model that utilizes virtualization technologies to abstract processing hardware into software form. Rather than inefficiently allocating one server to each user, virtualization allows providers to segment servers in such a way that multiple users can be housed on a single server.
The same virtualization techniques also allow providers to distribute workloads across multiple servers, providing SDDC customers convenient scalability. The SDDC model effectively turns a data center into a cloud provider, parceling out the data floor’s processing and storage power on an “as needed” basis. Virtualization also helps to improve efficiency, ensuring that computing resources aren’t being underutilized.
3. Hybrid Cloud Deployments
Although many organizations were early adopters of public cloud technology, the lack of control and pricing challenges has caused many of them to abandon purely cloud-based solutions. At the same time, private infrastructure brings its own set of problems. Increasingly, companies are turning to hybrid cloud architecture to provide them with the control and security they expect from a private network as well as the expansive power of public cloud computing services.
Hybrid clouds allow companies to store and manage valuable data assets on secure private servers and then shift them into a public cloud for various processing applications. Given the importance of big data analytics in today’s economy, having a network that offers secure and easy access to cloud-based service platforms is vital for business success.
4. Edge Computing
The rapid proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices has shifted the conventional architecture of many networks. Rather than forcing data to make the long journey back to a centralized server for processing, companies are keeping it closer to where it was generated on the network edge. Known as edge computing, this data center architecture uses the processing power of devices on the network edge to resolve requests and actions rather than relying on centralized processing resources.
The reorientation greatly reduces latency, which translates to faster performance for IoT devices and less service interruption for end users, whether they’re trying to access cloud resources or stream content. Edge data centers positioned in pivotal growth markets have helped organizations to extend their edge computing networks, servicing local users and reducing strain on distant hyperscale facilities.
With IoT edge devices gathering more and more information from users, edge computing strategies will help data centers better manage this data by only sending some of it back to the network’s central servers.
5. Artificial Intelligence
Perhaps no development has had a greater impact on data center efficiency than artificial intelligence (AI) programs that monitor and adjust performance over time. Predictive analytics can use historical operations data to identify problem areas and draw connections between various processes and energy usage. The most dramatic example of this was Google’s decision to hand over control of a data center’s cooling infrastructure to an AI program, which resulted in a 40 percent reduction in cooling costs. With AI applications, facility managers have a better idea of when data center components will need to be replaced or how a minor change in equipment deployment could impact energy costs over a period of time.
6. Automation

Data centers must be staffed by qualified IT professionals, and with the exponential growth of the industry, it’s likely going to be difficult to keep up. In fact, in 2018, experts were already identifying an aging workforce as one of the key challenges that lie ahead for the data center industry.
In response, remote management and automated processes will become more common, though many are already in use. In fact, troubleshooting infrastructure and network inefficiencies are already automated allowing existing staff to address those issues as needed. However, moving forward, there will be an increase in such processes and many of those will be in the hands of the business itself through real time monitoring.
7. Intelligent Monitoring
As noted above, intelligent monitoring, which allows a business to look in on its utilization, both physical and logical, and then address issues as needed, is a trend we’ll see grow in the next few years.. In this way, both management and monitoring are an automated process. You get real time data delivered to you, without an actual person to physically monitor for you.
Currently, most monitoring services capture a moment in time and provide that data as an opportunity to monitor. However, colocation service providers and data center solutions companies, like vXchnge, who already use real-time monitoring and put access to that data in your hand via a mobile application are ahead of the curve.
Real-time access means you’ve got real-time information which means your ability to predict your needs, areas of concerns, and measure your response is greater.
8. 5G
One of the primary drivers behind edge computing is the 5G network which and, in turn, the evolution of edge computing will drive 5G. Because 5G relies upon fast moving data and quick access through mobile spectrums, having data accessible, in edge facilities, will become even more important.
That said, 5G will also require upgrades and updates to some of the network components, hardware, and software utilized in data centers. Again, it’s expected that these upgrades, and the costs associated with them as well edge computing needs, will further drive data center business and the reliance on them as a business solution.
While it’s largely an under-explored realm at this point, in the next 5 years, with the increase in the IoT and mobile technologies, 5G has the potential to create seismic shifts in the data center landscape.
FAQ
1. How does green technology impact data centers?
Green technology, such as renewable energy sources and efficient cooling systems, can significantly reduce a data center’s carbon footprint and operational costs. Many modern data centers are adopting sustainable practices to be more environmentally friendly.
2. How do data centers ensure data redundancy?
Data redundancy is achieved through backup systems and disaster recovery solutions. Many data centers use multiple backup locations and cloud storage solutions to ensure data is safe and retrievable in case of any failures.
3. What is the role of blockchain in data centers?
Blockchain can enhance data security and transparency in data centers. It provides a decentralized ledger of all transactions, making data tampering more difficult and ensuring more secure data storage.
4. How do data centers handle cybersecurity threats?
Data centers employ multiple layers of security measures, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption, and regular security audits, to protect against cyber threats.
5. Are there standards or certifications for data centers?
Yes, there are several standards and certifications, such as ISO 27001 and the Uptime Institute’s Tier Classification, which set benchmarks for data center design, operations, and efficiency.
Final Words
In the digital age, data centers are the backbone of businesses, ensuring seamless operations, data security, and scalability. As technology evolves, so do the demands on these centers. Staying updated with the latest trends, from AI to 5G, is crucial for businesses to harness the full potential of their data infrastructure. By understanding and leveraging these advancements, organizations can ensure they are well-equipped for the future, driving growth and innovation.








