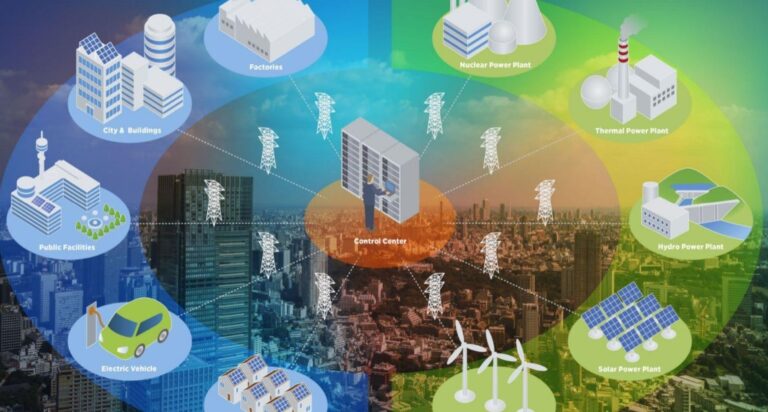
Growth is an important goal for almost any business. Consistent business growth can help companies attract new investors and talent, improve profits, and create some breathing room for emergencies—after all, losing a client/customer isn’t nearly as worrying for businesses with 10,000 accounts as they are for ones with 50 accounts.
However, growth is more than just adding new accounts and new employees—it means being able to scale all operations in the business. In today’s business environment, this often means having strong network scalability.
Why is network scalability important? How can you test your IT systems to determine what you need to do to achieve scalability? How do legacy systems affect your IT scalability?
Why It Matters
Scalability is a measure of how easily a business unit or process can be upscaled/increased or downscaled/decreased. Network scalability specifically references how easy it is for a business to add or remove bandwidth or processing capacity to their systems to keep up with demand without overspending.
Scalability for a network matters because:
- It impacts how well a business will be able to keep up with ever-evolving demands for network infrastructure.
- If a business’ growth outpaces its network capabilities, this can cause service disruptions that drive customers away. Maintaining high availability is crucial for keeping customers happy and business operations running smoothly.
- When demand for network infrastructure declines (such as during a seasonal business slump), being able to scale back infrastructure can help to reduce IT costs.
Long story short: having some IT flexibility can be incredibly valuable for any business. With the ability to scale easily to meet network infrastructure requirements, businesses can ensure stability, avoid service disruptions, and control costs.
How to Conduct Scalability Testing
Scalability testing is a method of testing IT systems at their “maximum” and “minimum” operating capacities to determine how the system may need to be modified to allow for projected growth. As noted by SoftwareTestingHelp.com, testing can occur at “the software, hardware and database levels. Once the maximum load is found out, developers need to respond appropriately to ensure that the system is scalable after a particular load.”
Some elements of the network infrastructure that a scalability test might assess include:
- Server Response Time: How long it takes for an application to respond to a user request. Shorter response times are more desirable because longer response times mean more delays for app users.
- Request Throughput: A measure of how many requests a given server, application, database, etc. can handle in a given period of time. This affects how many simultaneous users a network asset can handle.
- Bandwidth Consumption (Network Usage): A measure of how much data a given resource on the network consumes. Excessive use of network bandwidth can lead to problems that impact app performance and accessibility for users. Apps and resources that consume a lot of bandwidth are inherently more difficult to scale than ones that don’t.
The basic process for conducting scalability tests is relatively simple, though it may require specialized tools and the use of a secondary production environment to avoid causing disruptions while the test is being conducted:
- Establish Which Network Attributes You Wish to Test. Verify that there is a standardized expectation for which network performance attributes the test will measure. This includes ensuring that everyone is using the same terms for each metric—the list above could be a good starting point.
- Acquire Specialized Network Testing Tools. Search for programs that you can use to test network scalability. This can include finding a secondary production environment from a cloud service provider (CSP) or a collocated data center that has similar hardware and software to your main production environment.
- Set up Test Scenarios for Network Performance at High, Medium, and Low Loads. Using your network scalability testing tools, create tests of network performance at low, medium, and high loads to verify stability and performance at each level.
- Record and Analyze Your Results. Make a detailed record of the results from the test and analyze them to identify any potential issues that may affect your ability to scale your network in the future. This helps you prioritize the specific aspects of network performance that will have the biggest impact on your future ability to scale.
Managing Legacy Systems

With the advent of cloud computing models, scaling a business network has become significantly easier than it was in years past. For many businesses, scaling their network infrastructure is a simple matter of contacting their cloud application vendor and increasing their cloud app spend. However, this isn’t always the case.
Some businesses rely heavily on legacy systems that aren’t designed around a distributed cloud application service model. Instead, these systems were built around the assumption of a closed network or the use of a specific operating system (OS) and may not work with different architectures.
Managing legacy systems when planning for scalability can be difficult, but it is possible. Some things to keep in mind when dealing with these systems include the need to:
- Make a realistic assessment of how complicated migrating a legacy system will be;
- Audit existing IT assets to identify important elements of the network infrastructure that need to be replicated for the legacy system to work;
- Plan to adjust or even completely rework/replace some network elements when moving to a new data center since not all infrastructure elements may work on new hardware; and
- Consider upgrading legacy systems to newer systems that are more compatible with cloud computing, big data analytics, and high availability (always-on) solutions.
For more insights on creating visually appealing presentations that convey these concepts effectively, you might want to explore background slides that can make your message stand out.
Scaling Your Business with a Collocated Data Center
One of the simplest ways to scale up a business’ network infrastructure is to add new data centers (or to upgrade an existing data center with newer, more powerful servers). However, adding more data centers internally can be a major expense and challenge. Additionally, once this extra infrastructure is added, it can’t be removed—so this isn’t an ideal solution for addressing seasonal spikes in infrastructure use.
Yet, when cloud computing services don’t offer apps and solutions that work with your existing legacy systems, it may feel like you don’t have any other choice than to build infrastructure internally. However, there is another choice: using collocated data centers that combine the benefits of cloud computing with the control of having your own network infrastructure.
FAQ
1. What is the difference between scalability and elasticity?
While both terms refer to the ability of a system to handle growth, scalability is about the system’s capacity to increase its size or volume, whereas elasticity refers to the ability to scale up or down quickly based on demand.
2. How does virtualization impact network scalability?
Virtualization allows multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical server. This can enhance scalability by allowing businesses to quickly deploy new servers without the need for new hardware, making scaling more cost-effective and efficient.
3. Can cloud solutions always replace legacy systems for better scalability?
Not always. While cloud solutions offer excellent scalability, some legacy systems may have specific functionalities or integrations that aren’t easily replicated in the cloud. It’s essential to assess the business needs and potential trade-offs before making a switch.
4. How does security factor into network scalability?
As networks scale, security complexities can increase. It’s crucial to ensure that as the network grows, security measures are also enhanced to protect against potential vulnerabilities.
5. What role does IoT (Internet of Things) play in network scalability?
With the rise of IoT devices, networks may experience increased traffic and data processing needs. Ensuring network scalability is crucial to accommodate the influx of data from these devices without compromising performance.
Final Words
In the ever-evolving landscape of business and technology, ensuring network scalability is not just an option but a necessity. As businesses grow and adapt to changing demands, having a scalable network infrastructure ensures that they remain agile, efficient, and competitive.
Whether you’re leveraging cloud solutions, managing legacy systems, or exploring collocated data centers, the key is to stay proactive, informed, and prepared for the future.








