Non-governmental health plans, including private and self-insured health plans, are alternatives to public health coverage. They offer a range of benefits and challenges, depending on individual or business circumstances.
Choosing the right health plan requires a careful examination of cost, coverage, and accessibility to ensure it meets specific healthcare needs.
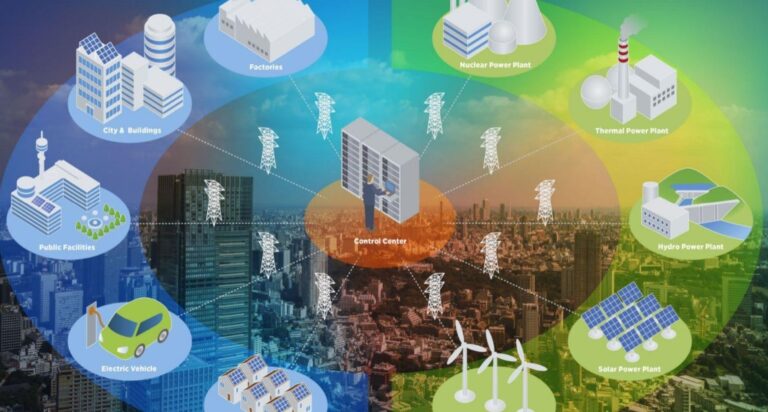
Private Health Insurance
Private health insurance is purchased directly through private companies, either as part of an employer-sponsored program or through individual policies.
These plans provide flexibility in coverage and allow individuals to choose options that best match their healthcare needs.
If you need to consult a professional who can help with understanding the non-governmental health plans, you can find help on this site.
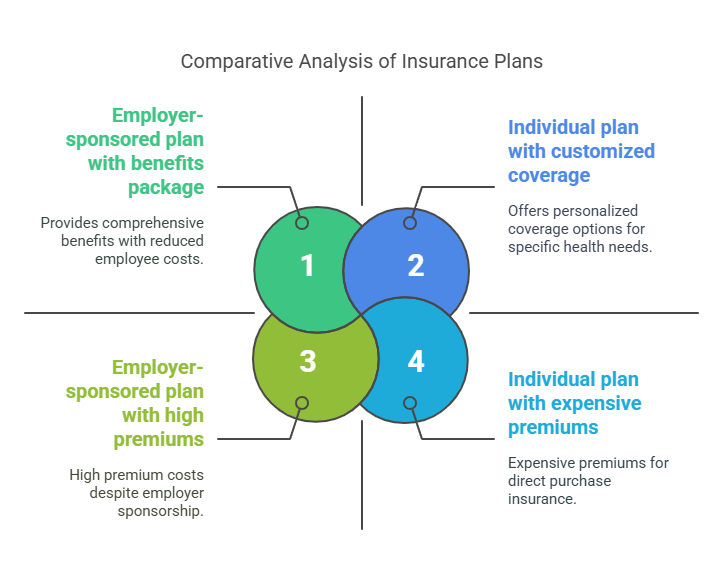
Employer-Sponsored vs. Individual Plans
Employer-sponsored private insurance is commonly part of employee benefits packages, covering a portion of premiums and reducing the cost burden on employees.
Coverage Options
Private insurance often includes options for dental, vision, and mental health services.
Policyholders can adjust their coverage based on their medical history and anticipated healthcare needs.
Access to Providers
Faster access to care is a major advantage, with reduced waiting times for specialist appointments and medical procedures.
- Cost Considerations: Private insurance premiums are generally higher than public insurance options.
- Out-of-pocket expenses, including deductibles and copays, can vary based on the level of coverage and location. Despite the financial burden, many individuals opt for private insurance because of the tailored coverage and quicker access to care.
Self-Insured Health Plans
Self-insured health plans are funded directly by employers, who assume financial responsibility for healthcare claims rather than paying fixed premiums to an insurance company.
While these plans are more common among large corporations, smaller businesses have also started adopting them to gain more control over healthcare costs.
- Employer Responsibility and Control: Employers manage healthcare funds and cover employee claims directly. Customization is possible, allowing employers to create plans that meet the specific health needs of their workforce.
- Cost Savings: Self-insured plans typically result in lower administrative costs since there is no need to pay external insurers. Improved cash flow due to the absence of fixed premiums allows businesses to allocate funds more efficiently.
- Risk Management: Financial risk is a key challenge since employers must cover high-cost claims directly. Stop-loss insurance is often used to protect against catastrophic losses, but it adds to overall costs.
- Administrative Complexity: Managing a self-insured plan requires compliance with regulations such as ERISA, HIPAA, and COBRA. Third-party administrators (TPAs) are typically hired to handle claims processing and regulatory requirements. Self-insured health plans provide greater control and potential cost savings but require careful management to avoid financial instability.
Pros and Cons of Private Health Insurance
It allows individuals and families to choose the type of medical services and providers they prefer.
Pros
The ability to customize coverage and gain quicker access to medical care are someday reasons why people opt for private insurance over public plans.
1. Flexibility and Customization
Private health insurance plans allow policyholders to tailor their coverage based on specific health needs. Unlike public insurance, which offers standardized coverage, private plans provide more freedom in selecting services and providers. Policyholders can add optional coverage for:
- Dental care
- Vision care
- Mental health services
- Pre-existing conditions
- Maternity care and fertility treatments
Flexibility extends to provider selection, allowing policyholders to visit preferred doctors, specialists, and hospitals without requiring a referral. Many private plans offer tiered coverage, allowing individuals to decide between basic, mid-range, and comprehensive packages.
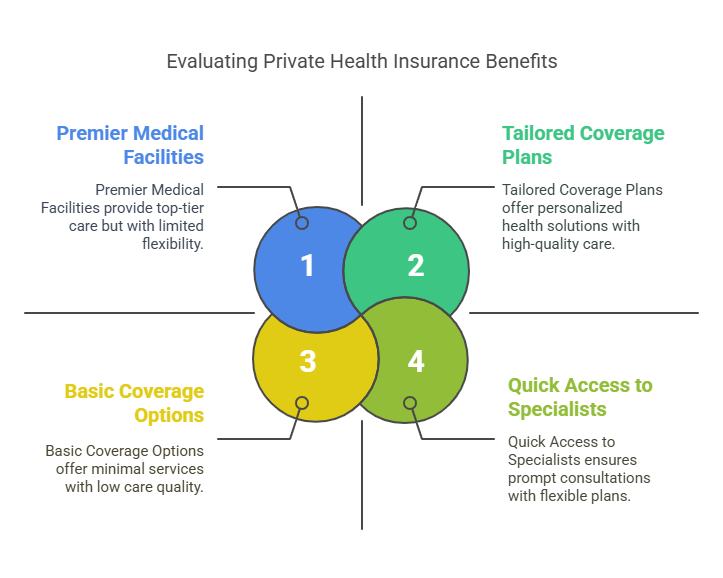
2. Wide-Ranging Coverage
Private insurance plans often provide access to a broader network of healthcare providers and specialized treatments that public insurance may not cover. This ensures a greater range of medical services and treatment options. Coverage typically includes:
- Advanced medical procedures
- Experimental treatments and clinical trials
- Specialist consultations without referral requirements
- Alternative therapies (e.g., acupuncture and chiropractic care)
3. Faster Access to Care

Public healthcare systems typically experience backlogs, leading to long waits for non-emergency treatments and specialist appointments.
Private insurance reduces these delays by providing:
- Faster access to specialists and diagnostic tests
- Shorter waiting times for surgeries and procedures
- Immediate appointment availability for routine and preventive care
Faster diagnosis and treatment typically lead to better health outcomes and quicker recovery times.
4. Higher Quality of Care
Private healthcare facilities tend to have better infrastructure and more modern equipment compared to public hospitals. This results in a more comfortable and efficient patient experience. Private facilities often feature:
- State-of-the-art medical technology
- Private rooms and enhanced patient amenities
- Higher staff-to-patient ratios, ensuring more personalized care
- Access to highly qualified specialists and top-tier medical professionals
The focus on patient comfort and service contributes to a more positive healthcare experience.
Cons

The financial structure of private insurance creates barriers for lower-income individuals, making it harder to access high-quality care.
1. High Costs
Private health insurance premiums are typically much higher than public health insurance rates. Out-of-pocket costs, including deductibles, copays, and non-covered services, can create a significant financial burden. Major cost factors include:
- Monthly premiums
- Annual deductibles (often higher with private plans)
- Copays and coinsurance rates for doctor visits and treatments
- Prescription drug costs
2. Profit-Oriented Model
Private insurance companies are businesses focused on generating profit, which can sometimes conflict with patient care priorities. Profit motives may lead to cost-cutting measures that limit access to certain treatments or medications. Profit-based decisions may result in:
- Denial of claims for high-cost treatments
- Restrictions on experimental or alternative therapies
- Limited coverage for chronic diseases or long-term care
- Higher rates for policyholders with pre-existing conditions
3. Disease-Specific Limitations
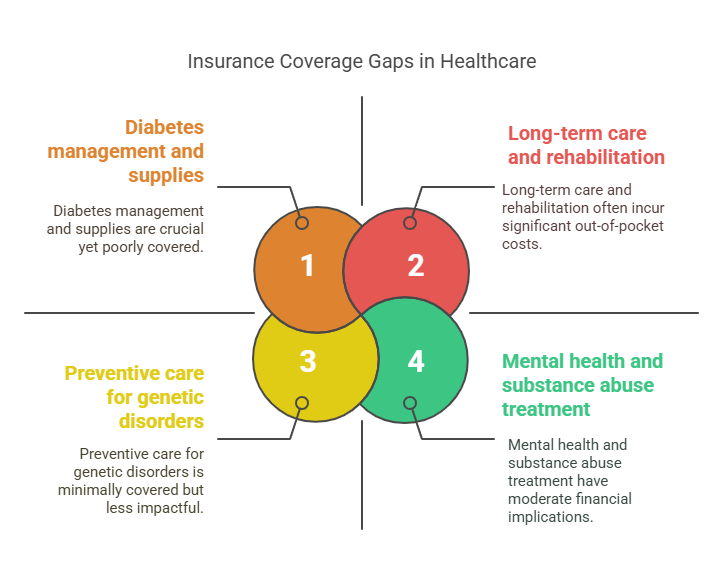
Common coverage gaps include:
- Diabetes management and supplies
- Mental health and substance abuse treatment
- Long-term care and rehabilitation
- Preventive care for genetic disorders
Policyholders often need to purchase supplemental plans or pay out-of-pocket for these services.
4. Unequal Access
Private health insurance tends to favor individuals with higher incomes, creating a gap in healthcare quality between socioeconomic groups. Those with limited financial resources may not have access to high-quality private care. Income-based disparities include:
- Limited access to premier hospitals and specialists for low-income policyholders
- Higher deductibles and copays for low-tier plans
- Reduced coverage for non-essential treatments
- Difficulty in affording advanced care or alternative therapies
It creates a system where healthcare quality is influenced by an individual’s financial status rather than medical needs.
The Bottom Line
Non-governmental health plans provide increased flexibility, faster access to care, and more comprehensive coverage options compared to public health insurance. However, they also come with higher costs and potential limitations in coverage for specific medical needs. Choosing the right plan requires balancing cost, coverage, and accessibility to ensure the best possible healthcare outcomes.
Related Posts:
- Should You Build Your Website Yourself or Hire a…
- Integrating Behavioral Health Electronic Health…
- What to Look for in Fitness Equipment to Enhance…
- Top Areas to Invest in Nusa Penida - A Closer Look…
- Why To Look For Customer Reviews Before Buying CBD Capsules?
- What To Look for When Choosing a San Antonio DWI Attorney







