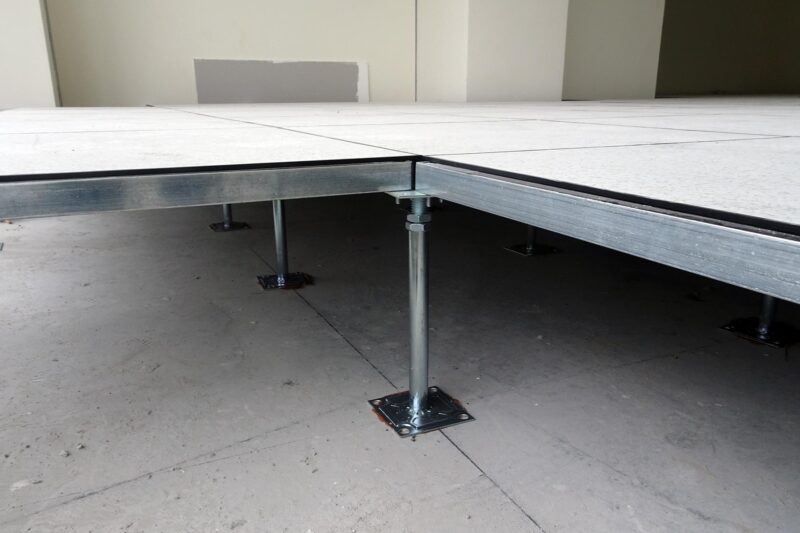
A raised floor in a data center is an elevated surface constructed two inches to four feet above a concrete foundation, creating a crucial space for cooling, electrical, and mechanical services. This innovative design is essential for efficiently distributing cold air, reducing the amount of air needed for cooling equipment, and improving temperature distribution across all cabinets.
Research has shown that raised floors can significantly reduce cooling loads by up to 40 percent. When combined with AI cooling solutions, the energy savings can be even more substantial.
The Importance of Cooling in Data Centers

Servers in data centers generate substantial amounts of heat, posing a significant challenge for designers and managers. Overheating servers can lead to severe consequences, including equipment failure and data loss. To mitigate these risks, maintaining proper temperature control is critical.
One common response to overheating is to add extra cooling capacity. However, this approach often stems from the misconception that the existing cooling infrastructure is insufficient. In reality, the problem frequently lies in poor airflow management rather than a lack of cooling capacity. Efficiently managing airflow can help maintain appropriate temperatures without the need for additional cooling resources.
Perforated Raised Floor Tiles
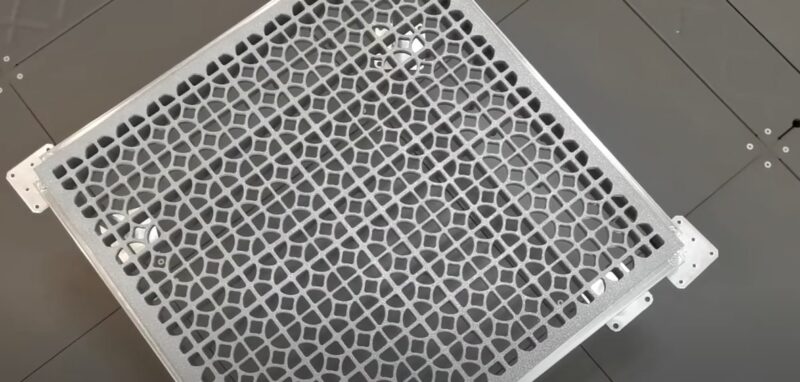
To maintain a cool environment in data centers, installing perforated raised floor tiles in cold aisles is a widely adopted practice. These tiles allow cold air to rise from the subfloor plenum, directly cooling the server racks.
Perforated tiles are generally not installed in hot aisles, except for maintenance tiles, which provide access to warmer environments for employee comfort. However, these maintenance tiles should not be left in place permanently, as they can restrict airflow and reduce cooling efficiency.
Grates are sometimes used as a temporary solution for hot spots within a data center. However, grates can exacerbate the issue by allowing up to three times more air to pass through compared to perforated tiles. Proper placement and management of raised floor tiles are critical. Installing too few tiles can lead to air recirculation, while too many can cause air bypass. If a choice must be made between recirculation and bypass, bypass is preferable.
Cabling and Equipment Upgrades
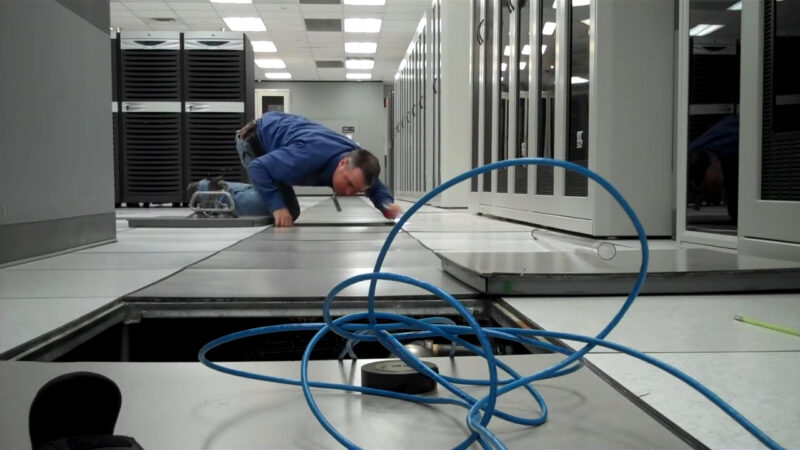

Raised floors offer significant advantages for equipment upgrades and new installations. This includes the installation of cabling and redevelopment of premises for other purposes.
Raised floors are especially beneficial when running large amounts of data center cabling, providing a more efficient and cost-effective solution compared to systems mounted near the ceiling. They also help consolidate hidden cables, physical ports, and power plugs, keeping the data center organized and functional.
Running data center cabling under raised floor tiles helps maintain a clutter-free and neat environment. Without overhead wiring systems, there is nothing to obstruct light fixtures, and technicians do not need ladders to access cabling.
Modifying the cabling layout involves simply identifying and removing the appropriate floor panel, avoiding the complications of overhead trays located near servers, light fixtures, and sprinkler systems.
Flexible Design for Future Needs
When designing a raised floor, data center engineers must consider the facility’s future development needs. This forward-thinking approach ensures that the data center can accommodate both current and future equipment.
The space beneath the raised floor tiles should be designed to allow efficient circulation of cool air. Once the floor is installed, regular maintenance is crucial to keep the area clean and free of obstructions.
A data center with a raised floor offers more versatility in terms of equipment deployment compared to a slab-based design. Rather than bolting cabinets to the slab and directing cooling from above, raised floor tiles allow for a more modular setup.
This flexibility enables the facility to relocate equipment without the need to install new cooling infrastructure, providing a significant advantage in terms of scalability and adaptability.
Raised Floor Tile Maintenance

Regular maintenance of the space beneath raised floor tiles is essential to prevent pollutants from posing a hazard to operations. Dust and debris can accumulate under the floor tiles and eventually flow into the equipment, leading to potential malfunctions.
Most data centers adhere to strict cleaning policies to ensure the subfloor space remains clean and free of contaminants. This reduces the risk of dirty air being pushed into servers, which can increase the likelihood of equipment failure.
Proper cabling layout is critical in facilities with raised floors. The cabling, although out of sight, should not be out of mind. Overcrowding cables in any area can significantly restrict or block airflow, preventing equipment from receiving adequate cooling. Data center managers must carefully monitor how cables are arranged, particularly when new lengths are laid or existing cabling is replaced.
Airflow Management
Effective airflow management is paramount to the success of any cooling strategy in a data center. Raised floors play a vital role in optimizing airflow, but the design and layout of the entire facility must be considered. Cold aisle containment (CAC) and hot aisle containment (HAC) are strategies that can be employed alongside raised floors to enhance cooling efficiency.
Cold aisle containment involves enclosing the cold aisle, which directs cold air from the raised floor tiles directly into the front of the server racks. This prevents the mixing of cold and hot air, ensuring that cold air reaches the servers more effectively. Hot aisle containment, on the other hand, involves enclosing the hot aisle, capturing the hot air exhausted from the servers, and directing it back to the cooling units. Both strategies can significantly improve cooling efficiency when combined with raised floors.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
Raised floors contribute to significant energy efficiency and cost savings in data centers. By improving airflow and cooling efficiency, raised floors reduce the energy required to maintain optimal temperatures. This not only lowers operating costs but also minimizes the environmental impact of data center operations.
Implementing energy-efficient cooling solutions, such as variable frequency drives (VFDs) and energy-efficient cooling units, can further enhance the benefits of raised floors. VFDs adjust the speed of cooling fans based on the real-time cooling demand, reducing energy consumption. High-efficiency cooling units, designed to work seamlessly with raised floor systems, can provide precise temperature control and further reduce energy usage.
Combining Raised Floors with AI Cooling Solutions
Artificial intelligence (AI) has revolutionized many aspects of data center management, including cooling. AI cooling solutions can analyze real-time data from sensors placed throughout the data center, making adjustments to optimize cooling performance. When combined with raised floors, AI can deliver even greater energy savings and efficiency improvements.
AI systems can predict cooling demands based on server load and environmental conditions, adjusting airflow and cooling capacity accordingly. This proactive approach ensures that the data center maintains optimal temperatures without overcooling, further reducing energy consumption. Additionally, AI can identify potential hot spots and recommend adjustments to raised floor tile placement, ensuring efficient airflow management.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of data centers is a growing concern, given their significant energy consumption. Raised floors contribute to reducing this impact by enhancing cooling efficiency and lowering energy usage. By minimizing the need for additional cooling capacity and optimizing airflow management, raised floors help data centers operate more sustainably.
Data center operators can further reduce their environmental footprint by implementing green building practices and energy-efficient technologies. This includes using renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, and designing facilities with energy efficiency in mind. Raised floors are an integral part of this approach, providing a foundation for sustainable data center operations.
Industry Standards and Best Practices
Adhering to industry standards and best practices is crucial for the successful implementation of raised floors in data centers. Organizations such as the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) provide guidelines for data center cooling and airflow management. Following these guidelines ensures that raised floors are designed and maintained to maximize their benefits.
Best practices for raised floor implementation include proper design and layout, regular maintenance, and continuous monitoring of airflow and temperature. Data center managers should also stay informed about advancements in cooling technologies and strategies, integrating them into their raised floor systems to enhance performance.
Conclusion
Raised floors remain a cornerstone of data center design, offering significant benefits for cooling efficiency, equipment deployment, and overall operational effectiveness. By optimizing airflow management, facilitating equipment upgrades, and providing a flexible design for future needs, raised floors contribute to the long-term success of data centers.
Related Posts:
- Why Learning Outside of School Is Just as Important
- 8 Important Developments in Data Center Technology
- What Are the Most Important Data Center Security Standards
- Horse Racing Laws: Most Important Rules to Protect…
- 5 Effective Website Strategy in Securing Important…
- Why Your Data Center Needs an Attestation of Compliance








